Since the beginning of the Russian invasion of Ukraine in February 2022, both sides involved in the conflict, both Ukraine and Russia, have been constantly striving to achieve military and political superiority. Within this confrontation, one side or the other seemed to gain the upper hand at some point. After the not-so-successful Russian offensive in the summer of 2024, at the moment, the initiative seems to belong to Ukraine, and this happened due to a surprise attack on the territory of the Kursk region of the Russian Federation.
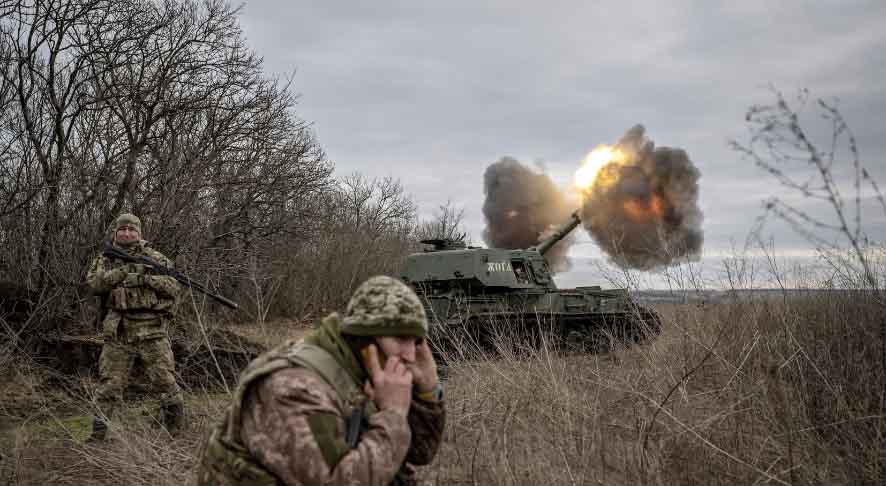
The Ukrainian offensive in Kursk Oblast began on August 6, 2024, and came as a surprise to both the Russians and Ukraine's allies. It was the largest operation conducted by the Ukrainian armed forces on Russian territory since the beginning of the war. At the beginning of the offensive, Ukrainian troops crossed the border into Russia, involving at least 1,000 soldiers supported by tanks and armored vehicles.
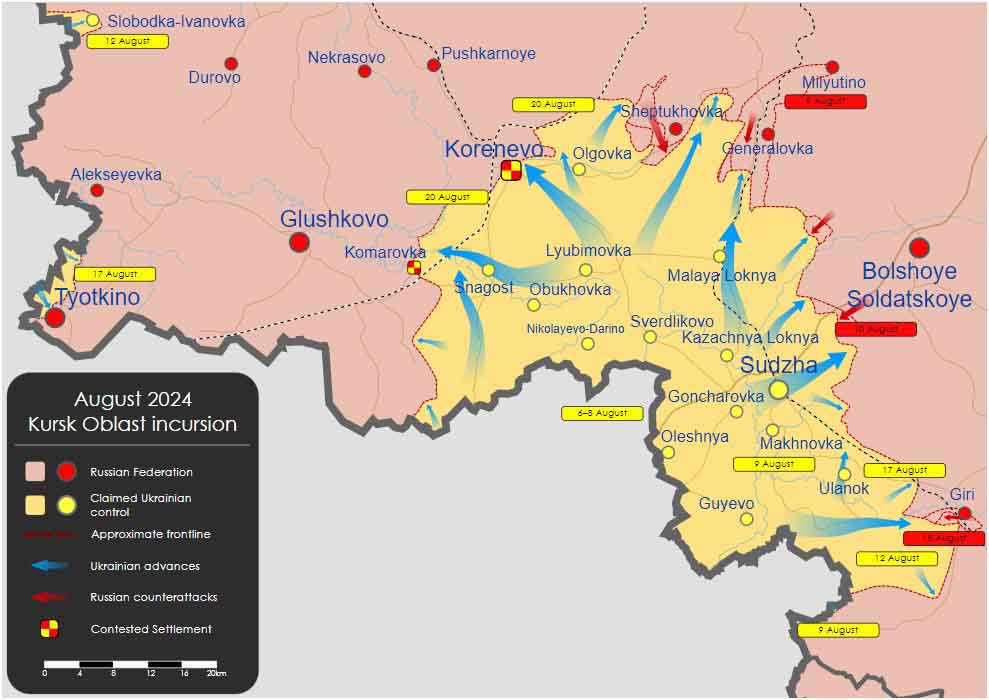
Kursk incursion, August 2024 (Source: Wikipedia)
As a result of these actions, Ukraine gained control over about 1,000 square kilometers of territory and 28 settlements in Kursk Oblast. And so, in recent weeks, Kursk Oblast, located in the southwestern part of Russia, has become one of the most important flashpoints of the conflict — at least judging by the headlines in newspapers and portals.
The Ukrainian offensive in Kursk Oblast, although at first glance it seems very risky, may have deep political, strategic, operational and tactical significance. Let us try to answer the questions that are troubling many now, namely what specific goals the Ukrainian side was guided by, and what will be Russia's possible reactions and the global consequences of this operation.
The Importance of Kursk
Kursk Oblast plays a key role in Russia's military and logistical infrastructure. It is a region directly bordering Ukraine, which is an important point of transfer of Russian forces to the Eastern Front. In addition, the oblast is an important energy hub, through which transmission lines and pipelines pass, supplying Russia and Western Europe with energy resources.
Historically, Kursk Oblast was the scene of the largest tank battle of World War II, fought between July 2 and August 23, 1943, not far from Kursk itself. The battle ended with a Soviet victory over the Germans, which was the first such breakthrough of the Nazi offensive and gave the strategic initiative to the Red Army until the end of the war.
The second reference to the name Kursk that could have symbolic meaning here was the submarine K-141 Kursk, belonging to the Russian Federation's Northern Fleet. This nuclear-powered ship, designed to combat large surface units, participated in large-scale maneuvers in the Barents Sea, and sank on August 12, 2000, along with all 118 crew members, as a result of an explosion on board.
The rescue operation of the survivors of the disaster was unsuccessful due to the low efficiency of the outdated Russian rescue equipment, the ossified bureaucratic system of the Russian Navy, the refusal of the Russian Defense Ministry to accept foreign aid, and, above all, the cynical and calculating political game of Vladimir Putin as the Supreme Commander of the Russian Armed Forces, who - already at the beginning of his first term as President of the Russian Federation - did not care about the lives of his sailors.
Strategic Goals of Ukraine
We do not know them for sure today, because the war is still ongoing. The Ukrainian leadership does not help in understanding, issuing inconsistent messages every now and then. We can only attempt to guess the strategic goals of the Ukrainian offensive in Kursk Oblast based on what is officially known on the subject.
Distraction from Donbas and Crimea: Ukraine may have wanted to shift Russia’s attention north, drawing its resources and forces away from key areas like Crimea and Donbas, where intense fighting is taking place. By striking Kursk, Ukraine may have wanted to force Russia to redeploy its forces, which in turn could relieve pressure in Donbas. So far, however, the Kremlin has left its eastern forces where they have been consistently successful, and instead deployed young and poorly trained conscripts to defend Kursk. In essence, Russia is trading Kursk for part of eastern Ukraine, and Ukraine is trading part of the east for Kursk.
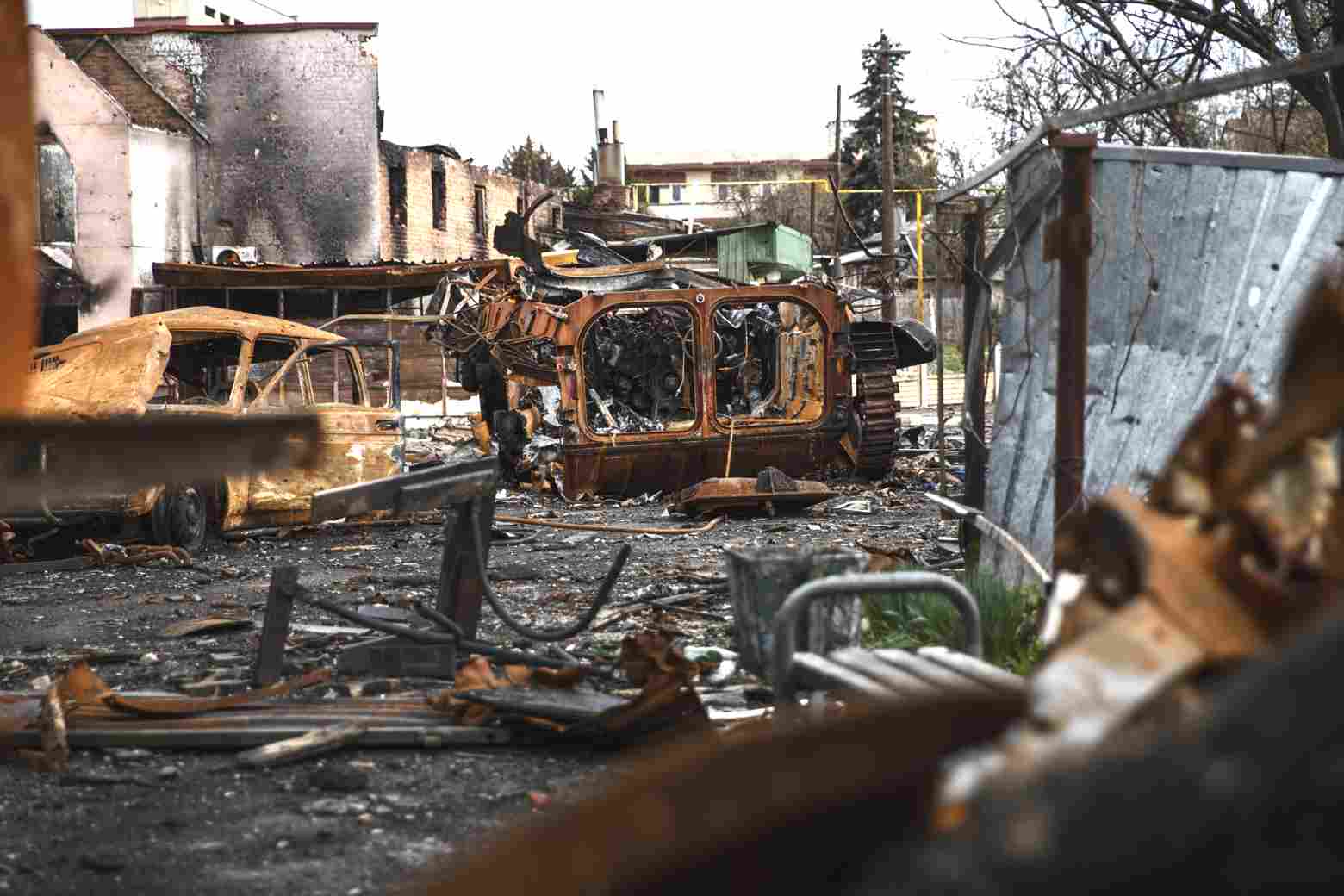
Destruction of Russian Logistics Infrastructure: A strike on the Kursk Oblast could disrupt Russian supply lines, which in turn could impact Russia's ability to conduct further military operations in Ukraine.
Demonstration of force: The attack on Russian territory is also a demonstration of force on the part of Ukraine, aimed at showing that Kiev is capable of conducting offensive operations on enemy territory. In the face of the war that has been going on for several years, Ukraine certainly wants to show that it is capable of not only defending itself, but also of conducting effective attacks in Russia itself. This is important because a large part of Russian society lives in the fog of propaganda that paints Ukrainians as simple peasants, incapable of conducting actions on their own. This propaganda also influences public opinion in the West quite effectively.
Impact on Ukraine's domestic political scene: An offensive into Russian territory could be seen as evidence of the Ukrainian government's effectiveness and determination in its fight for the country's sovereignty. Success in Kursk could strengthen the position of President Volodymyr Zelensky and his administration, increasing public support. But, it must be added, if unsuccessful, the offensive could be met with harsh criticism, especially from the opposition, and a failed operation could undermine confidence in the government and trigger a wave of political unrest, especially if the losses are significant.
Hopes for international reactions: An offensive on Russian territory could provoke positive reactions for Ukraine in the international arena.
First, Ukraine's allies in the West, including the United States and the European Union, may see this as evidence of Ukraine's determination to combat Russian aggression and thus be more inclined to continue to aid Ukraine.
Second, Ukraine may hope to expose the weakness of Russian forces and accustom the West to direct action on Russian soil and against strategic Russian targets using equipment and materials from NATO resources. The West may now see for itself that Russian threats are empty and not supported by any real actions. It may also agree to the use of advanced weaponry on Russian soil itself—an agreement that the Ukrainians have not fully had so far.
Bargaining chip: It is possible that Kiev's calculations take into account the possibility of achieving a better balance in possible negotiations. Part of Russian territory is now occupied, just as only Ukrainian territory was occupied so far. It is not a great leap of thought to imagine that it would be possible to negotiate now along the lines of: you give us our territories (e.g. Crimea), and we give you yours (i.e. the captured part of Kursk Oblast). This would be a kind of bargaining chip. However, it is hard to imagine that a mere part of Kursk Oblast captured would be equivalent to the area of Crimea or Donbas…
Domestic Destabilization in Russia: Ukraine could have counted on the Kursk offensive to unsettle and destabilize Russian public opinion, especially in the border regions. Growing public discontent could have weakened support for the Kremlin’s war effort and made it harder to mobilize new forces. However, this goal would be difficult to achieve, given Russia’s tight control of the media and the Kremlin’s propaganda efforts to downplay the significance of the Kursk invasion. It is also unclear whether most Russians care about Kursk’s fate at all.
Increasing pressure on Russia in international negotiations: Ukraine could also seek to increase pressure on Russia in the international context, forcing Moscow to answer questions about its domestic stability and ability to defend its territory. Such actions could weaken Russia’s position in the international arena, especially in the context of talks with Ukraine’s allies.
Cover for further actions: It is quite possible that the Ukrainian actions have a deeper basis and the Kursk offensive is just a cover, to divert attention, in order to carry out more strategically important actions for Ukraine, for example an attempt to regain Crimea. Maybe it is just an attempt to pull the wool over the eyes of the Russians, while the real offensive will take place somewhere and at a different time.
Mistake, or sabotage: Finally, it is quite possible that the Kursk offensive was either a poorly thought-out mistake or even a sabotage by anti-Ukrainian elements in the ruling elites in Kiev, aimed at weakening Ukrainian forces in the directions that actually matter, i.e., in Donbas. Note that the Russians did not transfer the attacking forces, e.g., in the direction of Pokrovsk, in Donbas, to the defense of Kursk and are still achieving success there. Do the still limited successes in Kursk region balance the territorial losses suffered at the same time in Donbas?
For Ukraine, an attack on Kursk Oblast is not only an attempt to weaken Russian military capabilities, but also a symbolic undermining of Russia's sovereignty on its own territory. From Kiev's perspective, striking such a sensitive region could weaken Russian military morale and force Moscow to disperse its forces over a larger area, which in turn could give Ukraine an advantage on other fronts.
In the second part of the article we will present an analysis of the operational and tactical conditions of the Ukrainian Kursk operation.